If you want to avoid ever being stranded near your car, anxiously waiting for a tow truck to arrive, this article is for you for replacing camshaft sensor.
It’s a common occurrence to experience engine failure in the middle of the road, leading to significant time loss. Or perhaps you’re aware that your engine isn’t performing optimally, but you’re attempting to push it to its limits before it inevitably breaks down.
Both scenarios are undesirable for any car owner. However, before you curse your engine, consider that the real culprit might be something more subtle and inherent: the camshaft sensor.
Have you recently replaced your camshaft sensor? Wondering what steps to take after replacing it to prevent future breakdowns and ensure your car runs smoothly? The key may lie in reprogramming the sensor, and this article will guide you through the process.
Contents
What Is a Camshaft Position Sensor, and How Does It Help?
You may have had your camshaft sensor replaced, but do you truly understand its function?
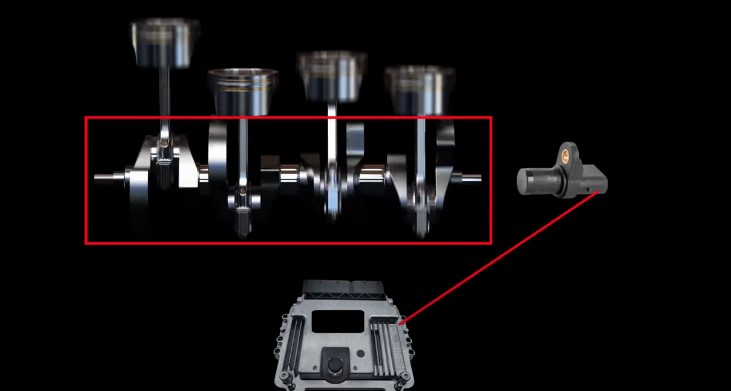
The camshaft position sensor is closely related to the camshaft’s motion, as its name suggests.
As the camshaft’s valves open and close, the sensor tracks these movements and collects data. These sensors are typically located above a carved ring on the camshaft.
Another component closely intertwined with the camshaft sensor is the crankshaft sensor.
By collaborating with the crankshaft sensor position, the camshaft sensor generates and adjusts AC signals when the shafts reach the Top Dead Center or the Bottom Dead Center positions.
Why is this information important? This data helps your car’s control modules make precise injector pulses and spark timing adjustments.
When Should a Camshaft Position Sensor Be Replaced?
Some people rush to have their camshaft sensor replaced as soon as they encounter error codes. While it’s true that error codes can indicate issues with the camshaft sensor, it’s not always wise to replace it at the first sign of trouble.
However, there are clear indicators that something is amiss with the camshaft sensor. Here are some signs to watch out for:
- Your car suddenly stalls frequently.
- The engine cranks but doesn’t start.
- The car starts after numerous attempts but immediately stalls.
- The dashboard displays erratic signals, often multiple at once.
- The sensor stops sending signals when it should be active.
- Your engine is overheated, aging, and the sensors have corroded.
How Should a Camshaft Position Sensor Be Replaced?
While camshaft sensor replacement is typically a job for professional mechanics and not suitable for DIY, it’s helpful to understand the process.
When your engine experiences operational instability and malfunctions, it suggests that the camshaft position sensor has failed.
To replace the sensor, follow these steps:
- Remove the bolts securing the sensor to the cylinder head.
- Disconnect the sensor from the electrical system.
- Install a new sensor in its place and reconnect it to the system.
How Much Does It Cost to Replace the Camshaft Position Sensor?
For those who haven’t replaced their sensors yet and are reading this article for guidance, replacing a camshaft sensor can cost anywhere from $120 to $300.
In some cases, accessing the sensor may require removing other components such as gaskets and the valve cover, which could add an extra $20 to $40 to the cost.
If you’re considering purchasing new parts, expect to pay between $50 and $200. As for labor costs, they can range from $70 to $100, depending on the mechanic’s fees.
Keep in mind that these are general costs, and the prices for sensor installation and parts may vary depending on your car’s make and model.
Luxury vehicles or opting for service at a local dealership may incur higher costs. Location also plays a role in price fluctuations.
What to Do After Replacing the Camshaft Sensor?
Once you’ve completed the sensor replacement, you have two options: reprogram it or leave it as is.
When Not to Reprogram:
If you’ve replaced the camshaft sensor but retained the old crankshaft sensor, the Engine Control Module (ECM) will determine the optimal ignition and injection timing.
It will also analyze the time intervals between signal pulses to and from the module and sensor, comparing them to existing data to determine the correct pulse separation.
If the readings are within optimal range, there’s no need to reprogram the sensor. And if you encounter error codes after replacement, inspect all wiring and connector issues. If the problem persists, the camshaft sensor is likely not the culprit.
When to Reprogram:
Depending on the mechanic’s service and the manufacturer’s recommendations, certain installations may require the sensor to undergo relearning.
This process resets the information previously stored in the data table, forcing the ECM to learn the meaning of the new sensor signals. In such cases, reprogramming the sensor is necessary.
Choosing not to reprogram can result in trouble codes and diminished engine performance due to low overall power output.
For the best results, opt for sensor reprogramming at your local dealership.
Final Words
You now understand the role of the camshaft sensor, know when to replace it, and have a grasp of the costs involved. But what should you do after replacing the camshaft sensor?
As this article has explained, you have the choice of reprogramming or leaving it as is. If clearing previous codes resolves the issue, there’s no need for reprogramming.
However, if differences in service have altered the sensor signals read by the Engine Control Module, reprogramming becomes essential.
In all cases, prioritize the option that restores your engine’s operation to normalcy.
You may also read: